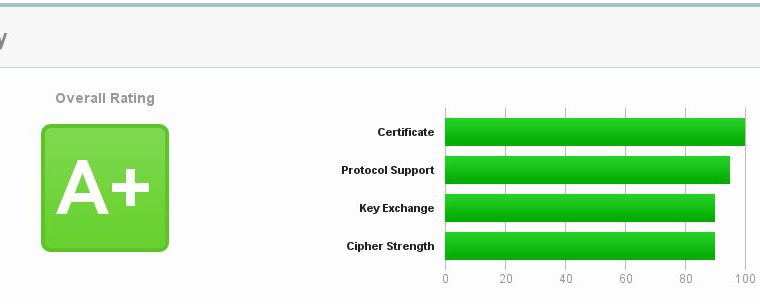
Task: setup SSL (https) settings in Nginx config file in order to get grade A+ there: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/
Best way – edit the /usr/local/vesta/data/templates/web/nginx/default.stpl
(the more, so if you will edit something from the panel, than Vesta CP will overwrite any changes made manually in the configuration)
Open in your favorite editor (of course nano :))
nano /usr/local/vesta/data/templates/web/nginx/default.stpl
Add next 4 fragments:
1. Add to field %ip%:%proxy_ssl_port% (in the same line):
ssl http2
2. After server_name:
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000;" always;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
3. After ssl_certificate_key %ssl_key%;
ssl_dhparam /home/admin/conf/web/dhparams.pem;
(first you need to generate dhparams.pem and put it in the right folder:
openssl dhparam -out /home/admin/conf/web/dhparams.pem 4096
)
4. (This fragment cannot just be copied from the browser, check for line breaks)
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA256:AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-SHA256:AES256-SHA256:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:AES:CAMELLIA:DES-CBC3-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!MD5:!PSK:!aECDH:!EDH-DSS-DES-CBC3-SHA:!EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:!KRB5-DES-CBC3-SHA';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
we get something like the following:
server {
listen %ip%:%proxy_ssl_port% ssl http2;
server_name %domain_idn% %alias_idn%;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000;" always;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl on;
ssl_certificate %ssl_pem%;
ssl_certificate_key %ssl_key%;
# ssl_dhparam /home/admin/conf/web/dhparams.pem;
error_log /var/log/%web_system%/domains/%domain%.error.log error;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA256:AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-SHA256:AES256-SHA256:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:AES:CAMELLIA:DES-CBC3-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!MD5:!PSK:!aECDH:!EDH-DSS-DES-CBC3-SHA:!EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:!KRB5-DES-CBC3-SHA';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
proxy_pass https://%ip%:%web_ssl_port%;
location ~* ^.+\.(%proxy_extentions%)$ {
root %sdocroot%;
access_log /var/log/%web_system%/domains/%domain%.log combined;
access_log /var/log/%web_system%/domains/%domain%.bytes bytes;
expires max;
try_files $uri @fallback;
}
}
location /error/ {
alias %home%/%user%/web/%domain%/document_errors/;
}
location @fallback {
proxy_pass https://%ip%:%web_ssl_port%;
}
location ~ /\.ht {return 404;}
location ~ /\.svn/ {return 404;}
location ~ /\.git/ {return 404;}
location ~ /\.hg/ {return 404;}
location ~ /\.bzr/ {return 404;}
include %home%/%user%/conf/web/snginx.%domain%.conf*;
}