It is assumed that you have a valid domain (the so-called FQDN), which you can use to enter the admin area. In my case, OVH provided a free domain of the form ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu, which means that I can use it to enter the admin area: https://ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu:8083/
Step-by-step set up Let’s Encrypt on the VestaCP admin panel (8083 port)
Step 1 – create a domain and find let’s encrypt files
First, in the admin panel, create your domain, if it is not already created. You can use the default user – admin, or any other. Include the use of ssl and let’s encrypt – you will get about the same as in the screenshot:
Let’s encrypt generates SSL certificate files and stores them in /home/[USERNAME]/conf/web (/home/admin/conf/web – in my case)
There is file list :
ssl.ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu.crt
ssl.ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu.ca
ssl.ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu.key
ssl.ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu.pem
2 Step – find where VestaCP stores its SSL files
It is not necessary to search, we simply know, that they is stored here 🙂
/usr/local/vesta/ssl
and files look so:
certificate.crt
certificate.key
You can carefully rename VestaCP old certificate files (although what prevents our simply removing them?):
mv /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.crt /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate_old.crt
mv /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.key /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate_old.key
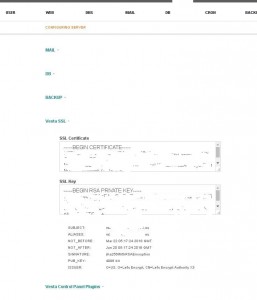
These 2 files are set in the form https://ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu:8083/edit/server/ -> Vesta SSL
3 step – force the Vesta-Nginx service to use SSL from your domain
Now you probably thought – we’ll just create symbolic links and everything will be fine … But …
But did you notice the problem? In the first case, we have 4 files, and although you can not pay attention to .pem – in the first form we have 3 fields: for CRT, KEY and CA, and in the second – only 2: for CRT and KEY.
Let’s Encrypt has a CA file that is reflected in the field: SSL Certificate Authority / Intermediate
How can this be taken into account in the VestaCP admin on port 8083?
I found for myself such a decision:
Make 1 symbolic link for the KEY file:
ln -s /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu.key /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.key
and in the second case – you can run this command:
sudo cat /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu.{crt,ca} > /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.crt
{crt, ca} is a regular expression on bash – it will defend you from writing 2 times the path to the file. It is very important that there is such a sequence – first crt, then ca. If you do the opposite – in the end, the vesta service will not work.
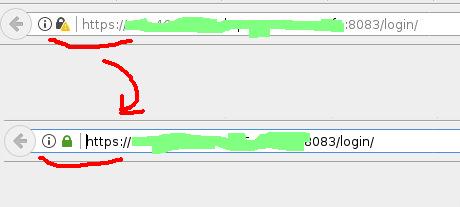
4 step – manually restart Vesta CP and check that everything works in the browser
Restart service:
service vesta restart
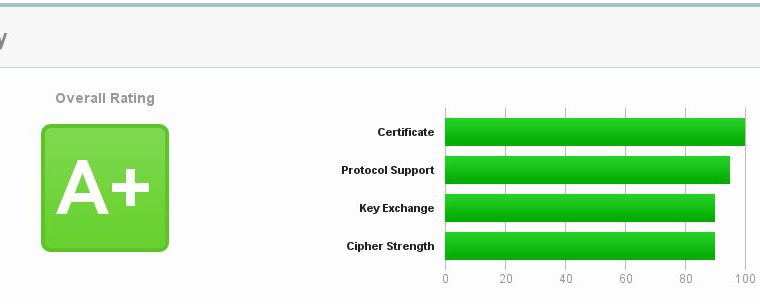
Open your domain in the browser with port 8083 and now SSL must be “protected”.
Step 5 – add the “certificate.crt” update task to the cron scheduler
We need to add the following task to the cron scheduler:
30 5 * * * sudo cat /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.ns123456.ip-x-y-z.eu.{crt,ca} > /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.crt && sudo service vesta restart
(look at what time the system cron “let’s encrypt update” task works and you’ll see something like this:
15 5 * * * sudo /usr/local/vesta/bin/v-update-letsencrypt-ssl
it is logical, if our task will be carried out later)
Done!